The TriTom platform based on Photoacoustic Fluorescence Tomography (PAFT) technology provides unparallel capabilities forwhole body imaging and in vivo characterization of small animal models. Complimentary 3D imaging modalities are integrated into a single powerful instrument by enabling co-registered Photoacoustic Tomography (PAT) and Fluorescence Molecular Tomography (FMT). Utilizing an innovative, compact configuration, simultaneous co-registered collection of orthogonal photoacoustic and optical projections can be acquired. The platform provides high-resolution robust anatomical registration of optical biomarkers, while maintaining high molecular sensitivity. A broad spectrum of preclinical research applications include cancer, toxicology, tissue engineering and regeneration, cardio vascular and developmental biology.
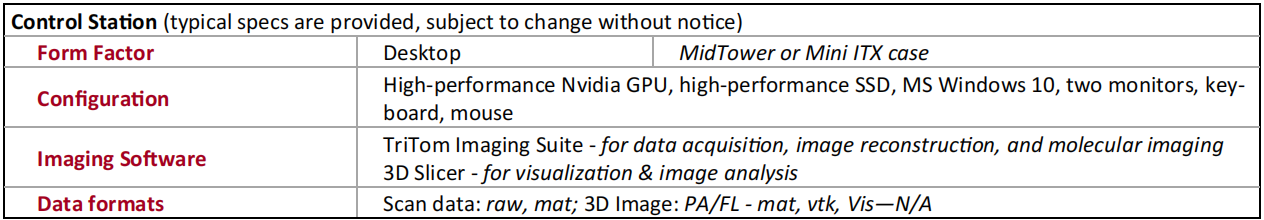
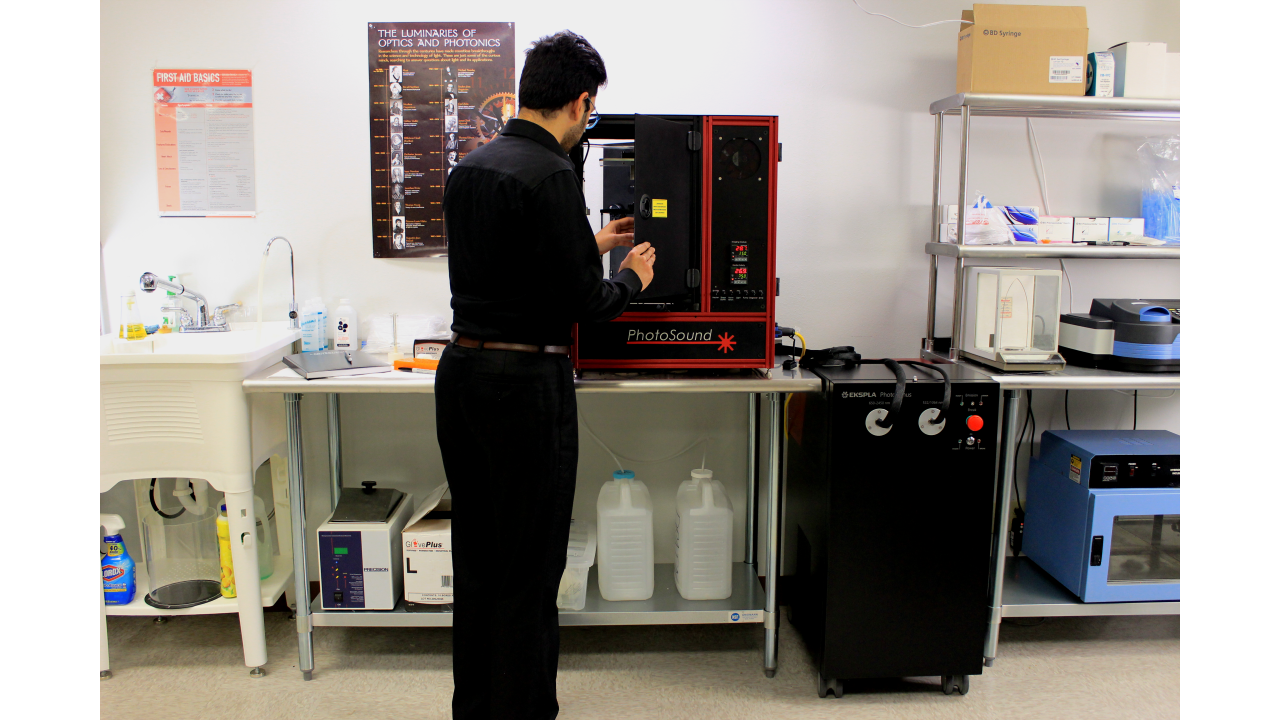
Bench-topDesign

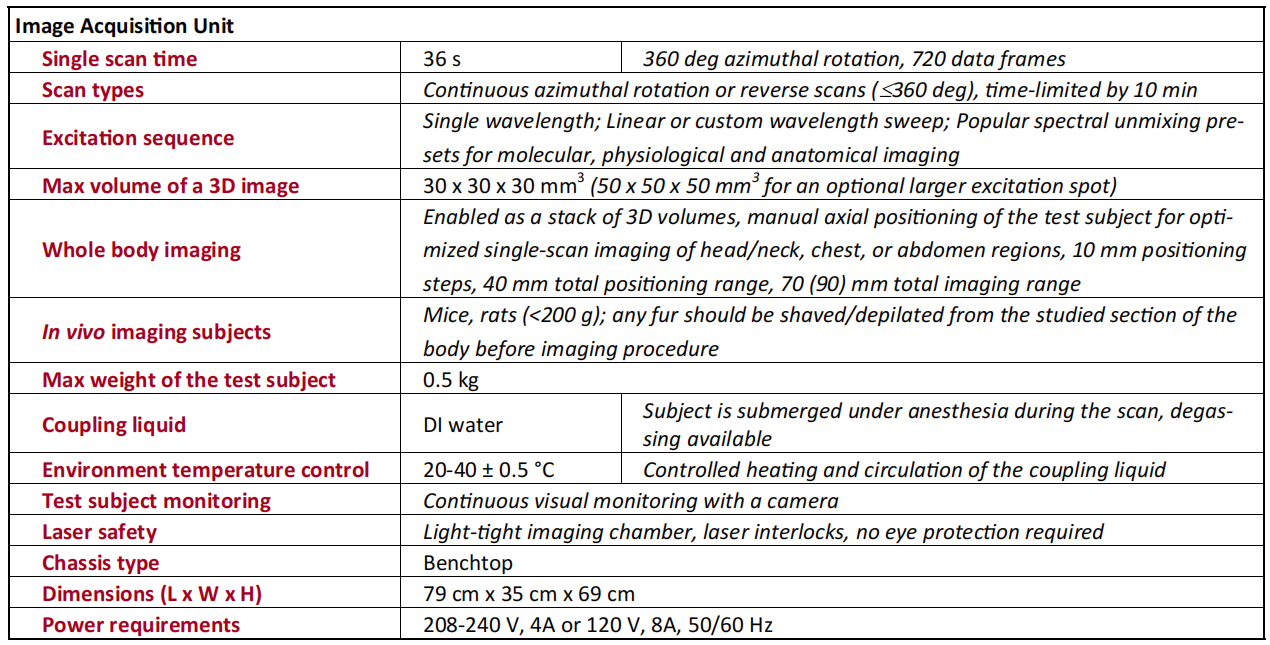
Working Principle

Application Area (See Application fordetails)
Anatomical Brain Imaging

Fig. 1: 7 mm maximum intensity projection(MIP) slabs of 750 nm excitation PA reconstruction volumes. Dorsoventralview of the mouse’s scalp. (1) transverse sinus; (2) superior sagittal sinus; (3) confluence of sinus; (4)auricular artery; (5) cerebral artery; (6) ophthalmic artery; (7) jugular vein;(8) brachial artery; (9) CuSO4 tube.
Imaging Mouse Spine
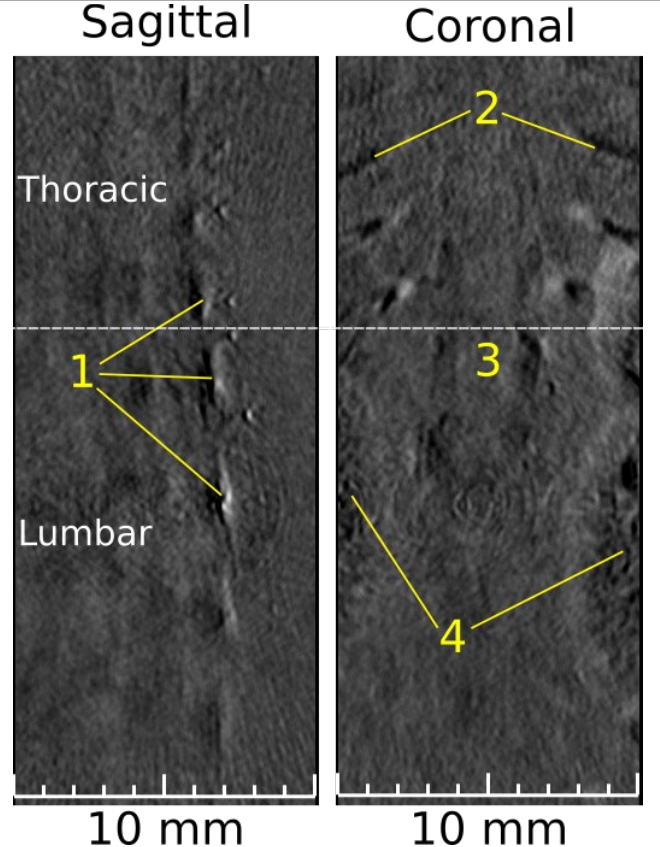
Fig. 2: PAT 2D slices, sagittal and coronalviews, excited by 850 nm. (1) Multiple thoracic and lumbar vertebrae; (2) ribs;(3) grey/white matter; (4) kidneys. Thoracic and lumbar sections are separatedby the dotted-white line.
Imaging Tumor Xenograft
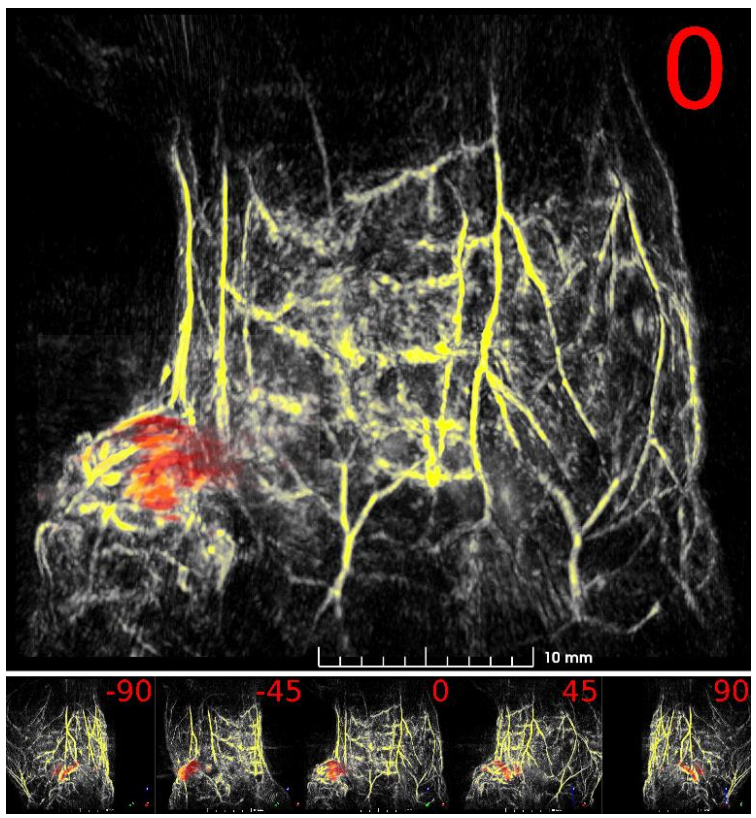
Fig. 3: Maximum intensity projection volumerender of the scanned mouse. 532 nm volume is colored yellow, 800 nm tumor volumeis colored red. Angle of rotation is displayed in the top-right corner of eachview.
Image-guided Delivery

Fig. 4: Photoacoustic image-guided delivery of plasmonic-nanoparticle labeled mesenchymal stem cells to the spinal cord (Donnelly,et al[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18: 6625?6632)
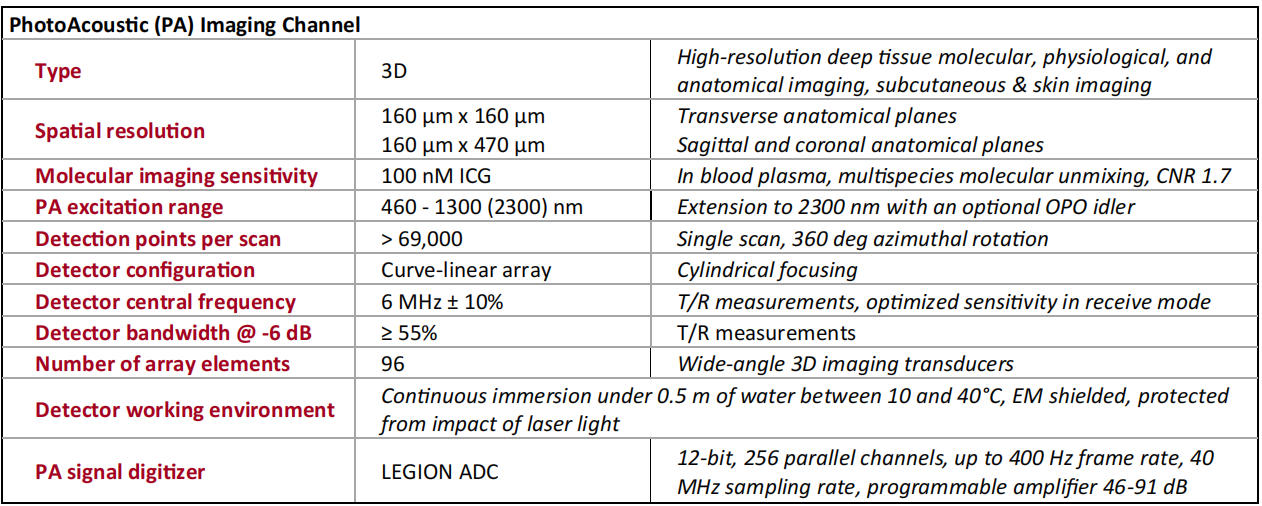
Specifications
36 sec single excitation wavelength scan duration
3D PAT reconstruction time: 6 min
3D FLT reconstruction time: 12 min
150 μm (x & y axes) 500 μm (z axis) PAT resolution
16 line pairs/mm FLT resolution
μa10 = 0.1 cm-1 PAT sensitivity (equals ~1 μM ICG in water)
30,000 virtual channels
30 x 30 x 30 mm visualization volume
Excitation wavelength: 670-2600 nm
Features
Imaging chamber with optimally arranged optical excitation ports andsafety interlocks on dual access doors
96-channel data acquisition unit optimized for detection of photoacoustic waves
EMI protected 96-channel curved transducer array
sCMOS camera covering a broad range of fluorescent and bioluminescent emission
Temperature control unit maintains sample environment within ± 0.1°C
Water control unit maintains clean, heated sound coupling medium with fill/drain/degassing
Durable key slot extrusion housing with safety interlocks
Precision rotary stage enabling tomographic scan of the sample
Built-in life support delivers oxygen/anesthesia directly to the sample
Anatomical Brain Imaging

Fig. 1: 7 mm maximum intensity projection(MIP) slabs of 750 nm excitation PA reconstruction volumes. Dorsoventralview of the mouse’s scalp. (1) transverse sinus; (2) superior sagittal sinus; (3) confluence of sinus; (4)auricular artery; (5) cerebral artery; (6) ophthalmic artery; (7) jugular vein;(8) brachial artery; (9) CuSO4 tube.
Imaging Mouse Spine

Fig. 2: PAT 2D slices, sagittal and coronalviews, excited by 850 nm. (1) Multiple thoracic and lumbar vertebrae; (2) ribs;(3) grey/white matter; (4) kidneys. Thoracic and lumbar sections are separatedby the dotted-white line.
Imaging Tumor Xenograft

Fig. 3: Maximum intensity projection volumerender of the scanned mouse. 532 nm volume is colored yellow, 800 nm tumor volumeis colored red. Angle of rotation is displayed in the top-right corner of eachview.
Image-guided Delivery

Fig. 4: Photoacoustic image-guided delivery of plasmonic-nanoparticle labeled mesenchymal stem cells to the spinal cord (Donnelly,et al[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18: 66256632)